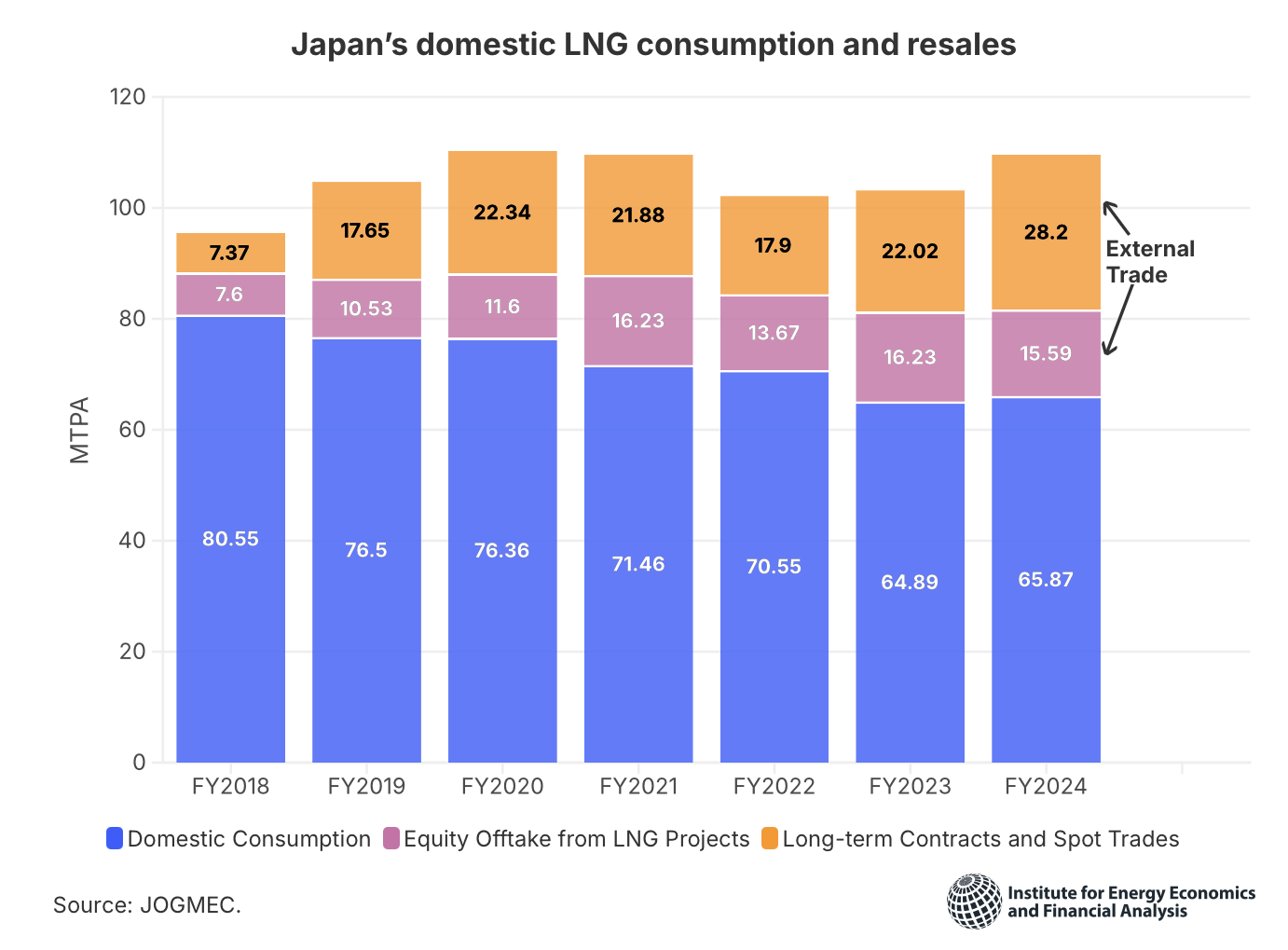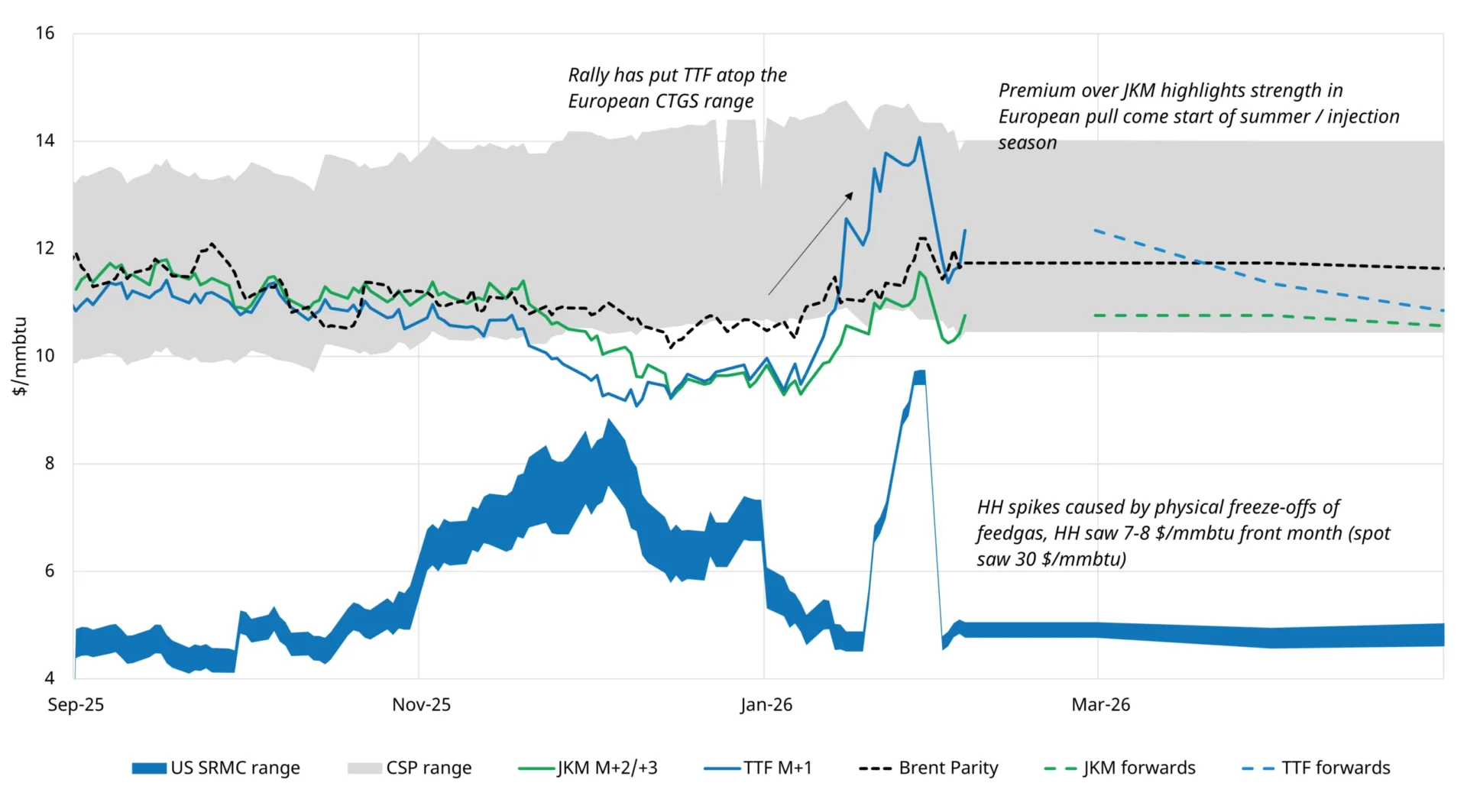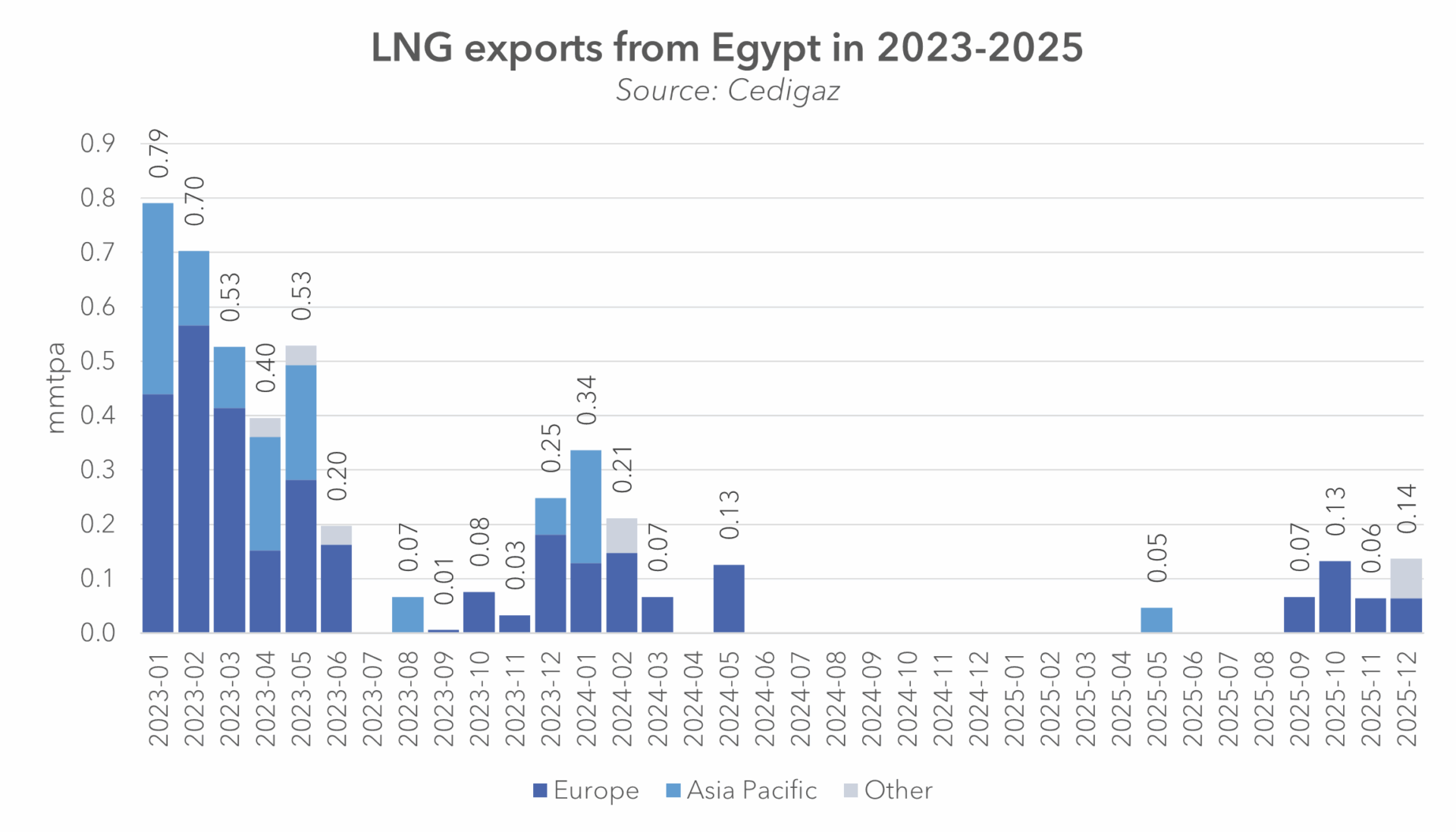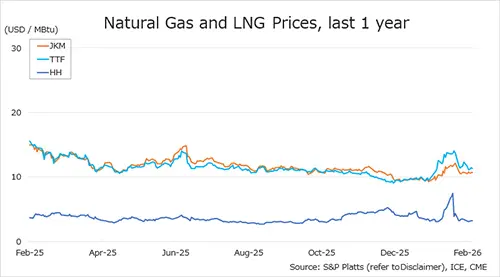
China is the fastest growing natural gas consumer in the world. In 2016, the first cargo of LNG from the U.S. arrived at China.
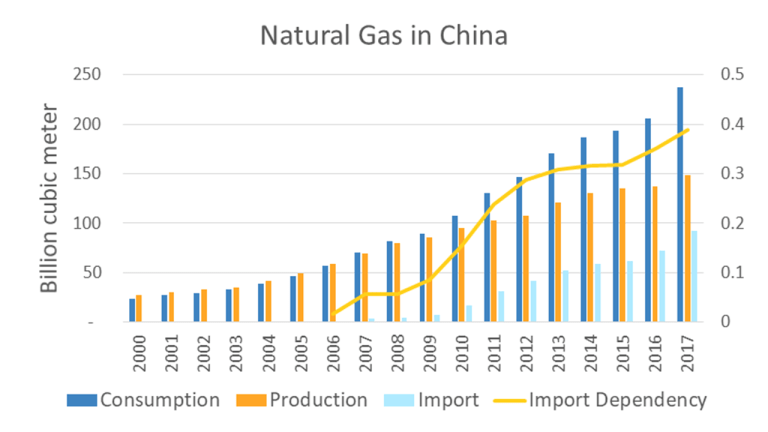
The Chinese government has initiated projects and campaigns to promote natural gas in replacing coal for factories and residential heating for addressing the main sources of air pollution. In 2017, China’s natural gas consumption increased by 15 percent, and its import grew by 28 percent; import dependency raised from zero in 2005 to 39 percent in 2017. In spite of its high cost and seasonal shortages, natural gas creates tremendous social benefits. Air quality in metropolitan areas improved between 21 percent to 42 percent during the first phase of the National Air Quality Action Plan (2014-2017), having yielded significant social and health gains.
The Chinese government is expected to wage the second phase of the anti-air pollution campaign in 2018, expanding the effort of cleaner fuel replacement. In addition, the government has also acknowledged the crucial role of natural gas in the climate and air quality battle as a “bridge fuel” to deepen renewable energy penetration.
Disclosed in its National Energy Strategy, China plans to increase the share of natural gas to 15 percent of the energy mix by 2030. If China’s primary energy consumption reaches 5.5 billion tons coal-equivalent by 2030, natural gas consumption would reach about 650 bcm accordingly, increasing by 2.7 times from the 2017 level.
Source: Jiaqi Lu & Ye Qi (Brookings Institute)
See LINK below to view the full article on the Brookings website