China lost its position as Australia’s top export destination in FY 2022 with 25.0 Mt (38%) of Australian export volume, less than 28.3 Mt (41%) in FY 2021.
In the 11 months to May Chinese LNG imports decreased by 4% while imports from Australia fell by 12% to 25.0 Mt from 28.3 Mt in the corresponding period in 2021, with the result that Australia’s market share fell to 38% from 41% a year earlier.
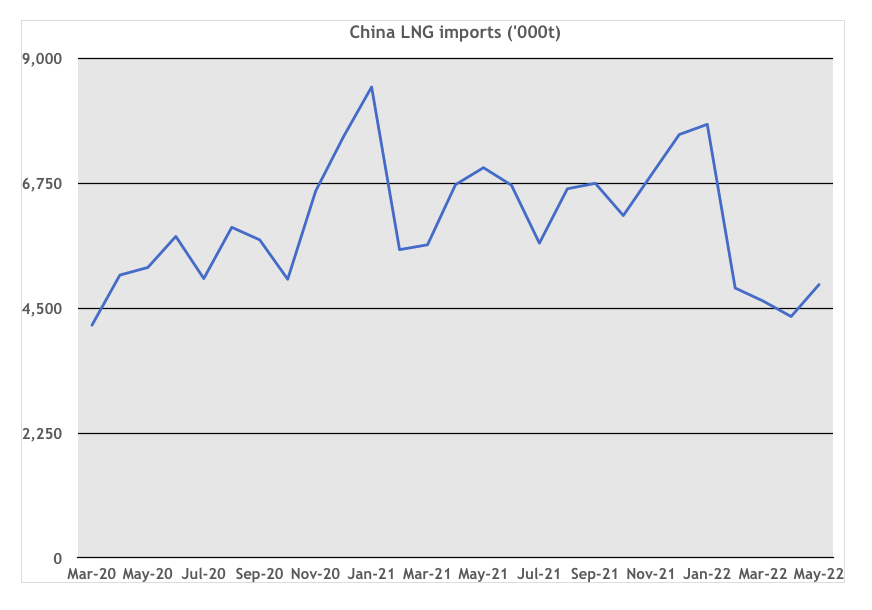
China has been the world’s fastest growing LNG market. However, this came to an abrupt halt in the first half of this year, with imports in April at the lowest level since early 2020 (Figure 1). The fall reflects Covid lockdowns and the slowing of the Chinese economy.
Figure 1 China LNG imports (‘000t)
 Source: EnergyQuest, Chinese Customs
Source: EnergyQuest, Chinese Customs
However, the fall in Australian China deliveries of 3.3 Mt was the largest of any supplier to China and was offset by increased China deliveries from Qatar (+2.3 Mt) and the US (+1.0 Mt).
The biggest fall in Australian exports to China was from Gladstone, which delivered 200 China cargoes in FY 2022, down from 238 cargoes a year before.
Deliveries from the west coast were also down but not as much, from 201 cargoes to 190 cargoes. However, notwithstanding the drop in China cargoes from Gladstone, the east coast more than offset this with increased cargoes to Japan, Korea, Malaysia, Singapore and Thailand.
Japan imports rose to 26.7 Mt (33%) of Australian export volume, up slightly from 26.6 Mt (34%) in FY 2021. Japanese LNG imports decreased by 6% in the 11 months and with steady Australian volumes, Australia’s market share increased from 37% to 40%.
Korea continues to be Australia’s third most popular export destination, importing 11.3 Mt in FY 2022, compared to 8.0 Mt in 2021.
EnergyQuest estimates Australia exported a record 82.6 Mt of LNG in the 12 months to 30 June 2022, well up on the 77.3 Mt in FY 2021, and more than the previous record set in FY 2020 of 79.3 Mt. This is a good result given Prelude was shut-in for over four months of the year, and the depleting field supply at NWS and Darwin.
Australian projects operated at average 93% of nameplate capacity of 88.6 Mtpa. QCLNG, Gorgon, Pluto and Ichthys all operated at over 100% of their nameplate capacity for FY 2022, with Pluto operating at almost 10% above its nameplate capacity.
Western Australian production was up by 9% on FY 2021 to 46.9 Mt and the Northern Territory was up, by 7% to 11.7 Mt.
The east coast had record production in FY 2022 of 24.0 Mt, up 3% from FY 2021.
The three Gladstone projects operated at 92% of nameplate capacity, with 6 months over 2.0 Mt.
Western Australia continues to dominate Australian LNG exports, supplying 57% of national exports, while Queensland produced 29% and the Northern Territory produced 14%. The Gorgon project in Western Australia was the largest contributing project, followed by the North West Shelf.
Gorgon’s production rose almost 45% in FY 2022 due to the restart after shutdowns required to repair cracks in the cooling kettles on all three trains during FY 2021. Prelude had the highest percentage growth, up 92.4% on production volumes from FY 2021 to produce 2.0 Mt in FY 2021. Ongoing safety issues once again saw production halted from Prelude for four months from December 2021.
Massive increase in LNG export revenue for FY 2022
EnergyQuest estimates total FY 2022 export revenue was A$70.18 billion, up 130% on the A$30.48 billion in FY 2021. Export income was driven by higher export volumes and much higher oil prices.
20 July 2022
Source : EnergyQuest