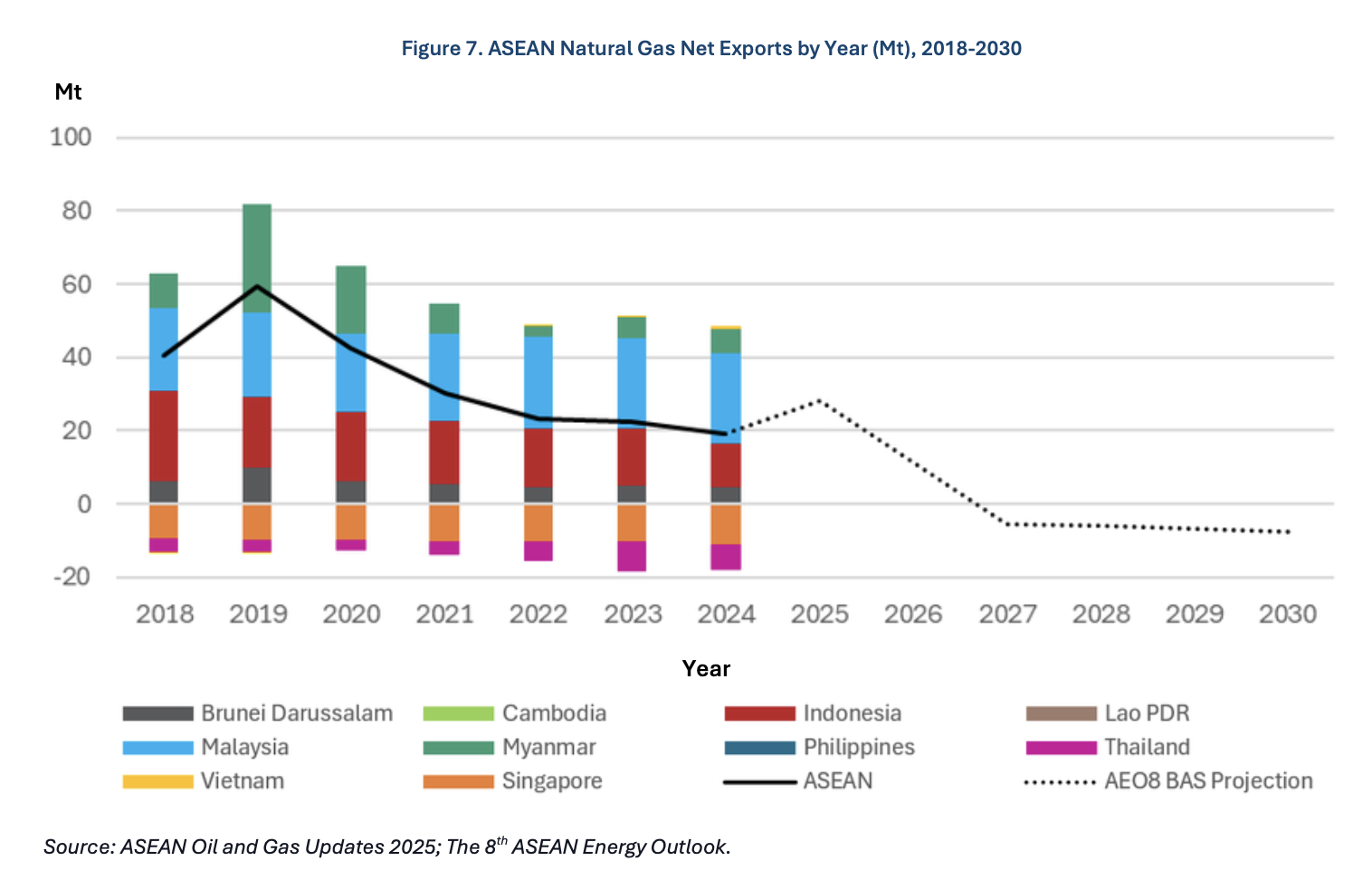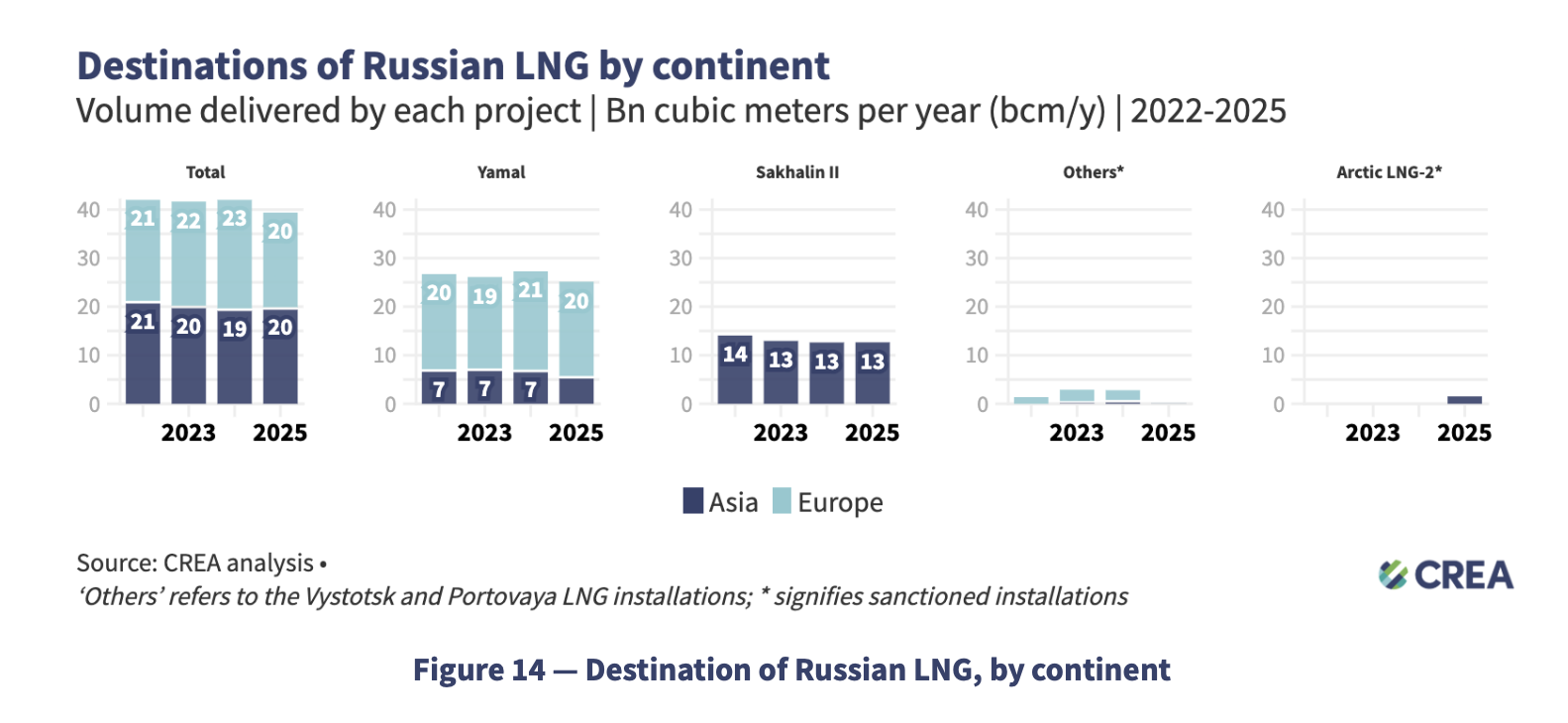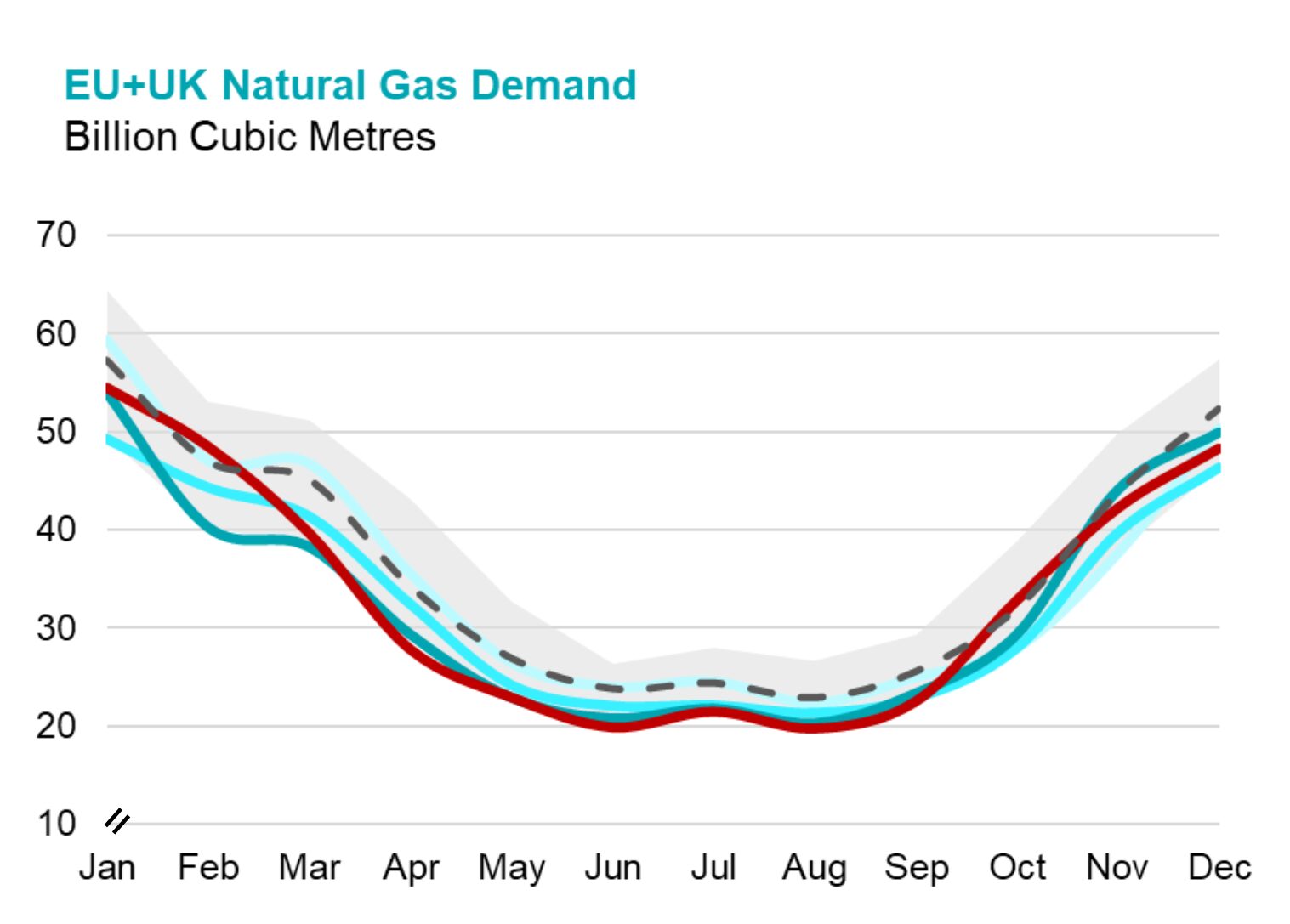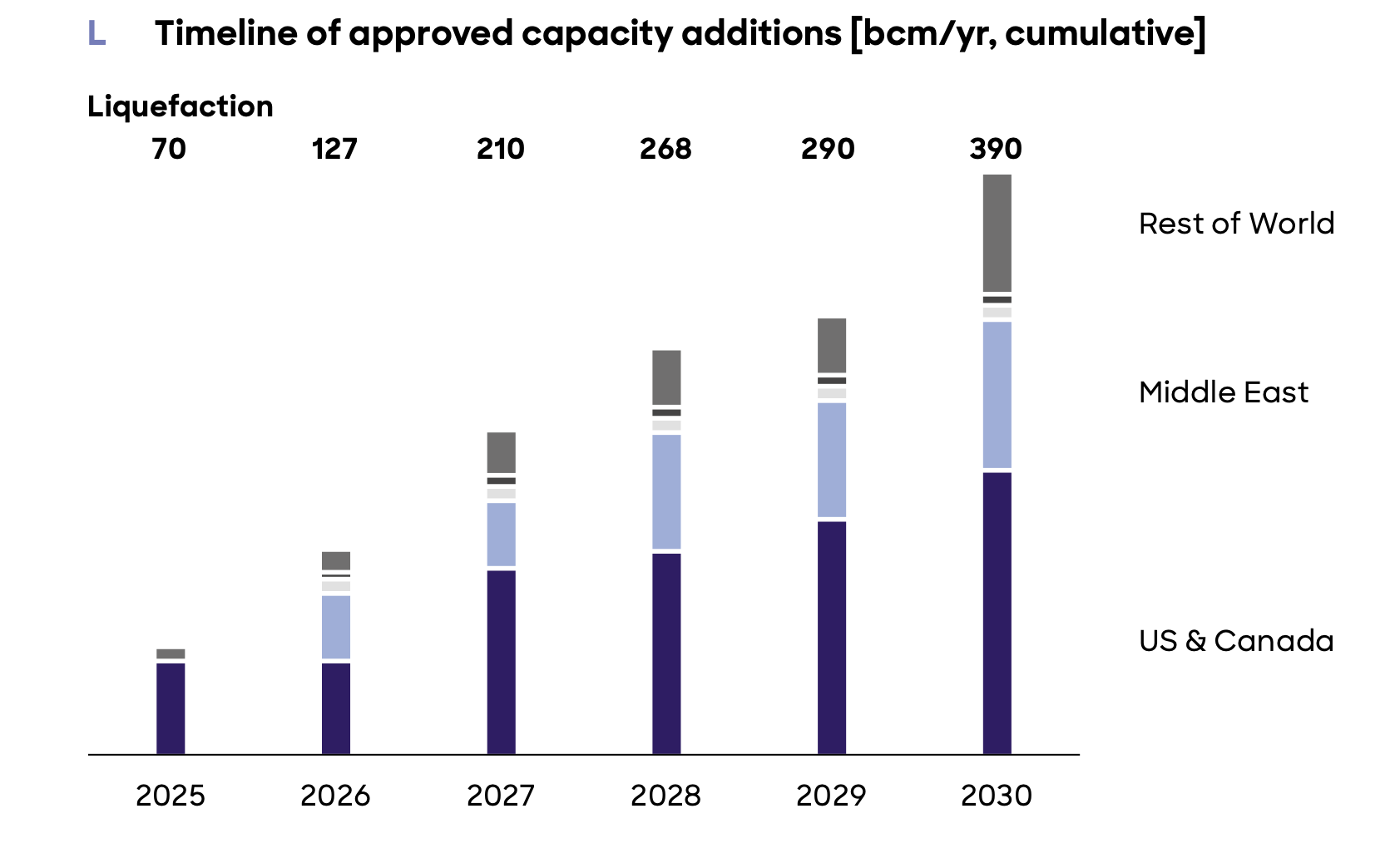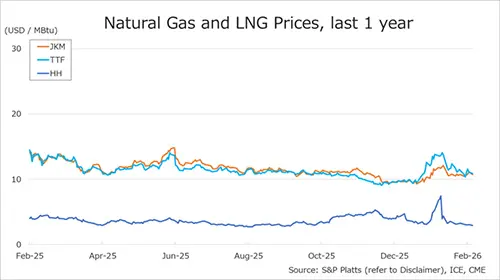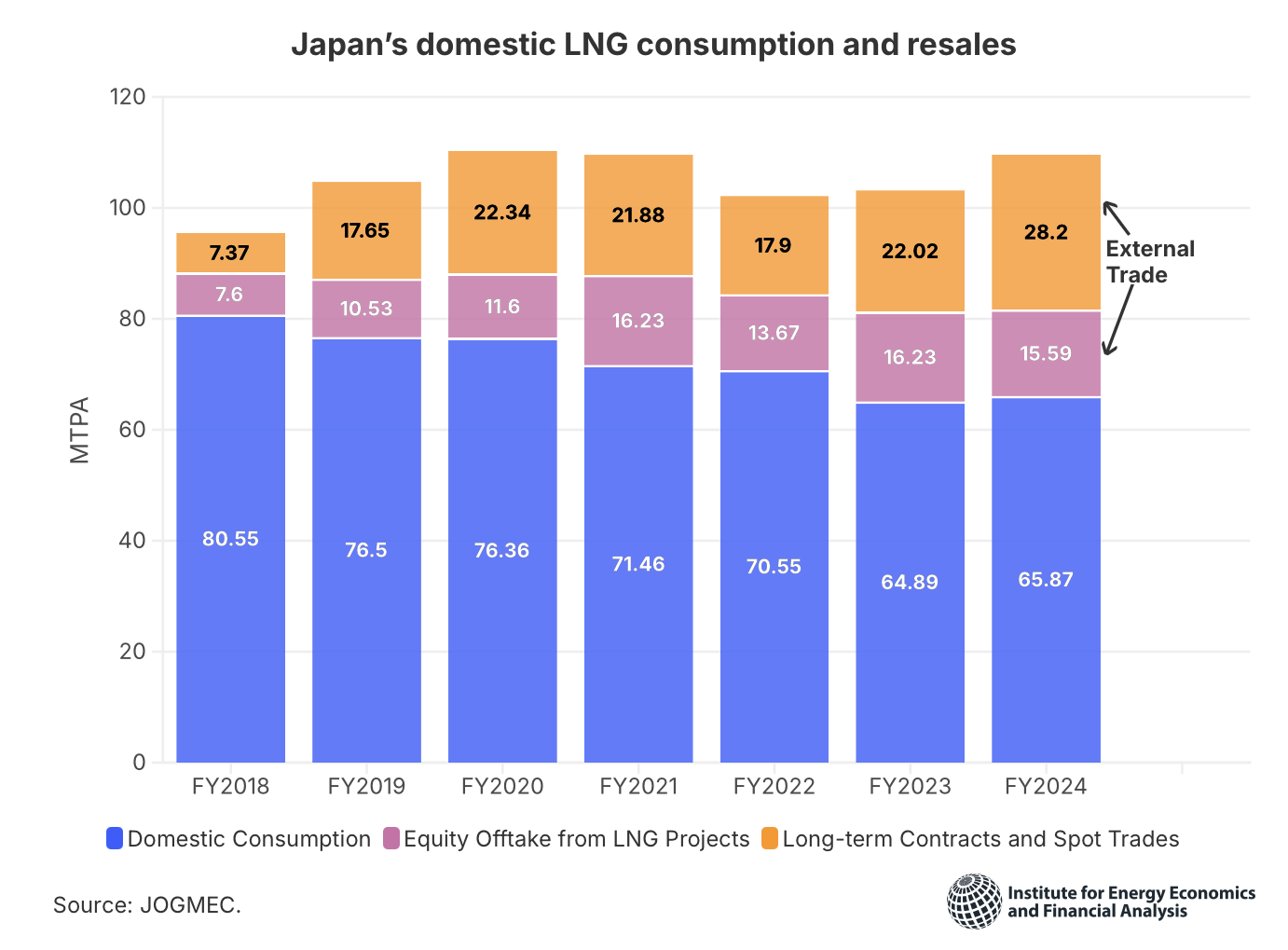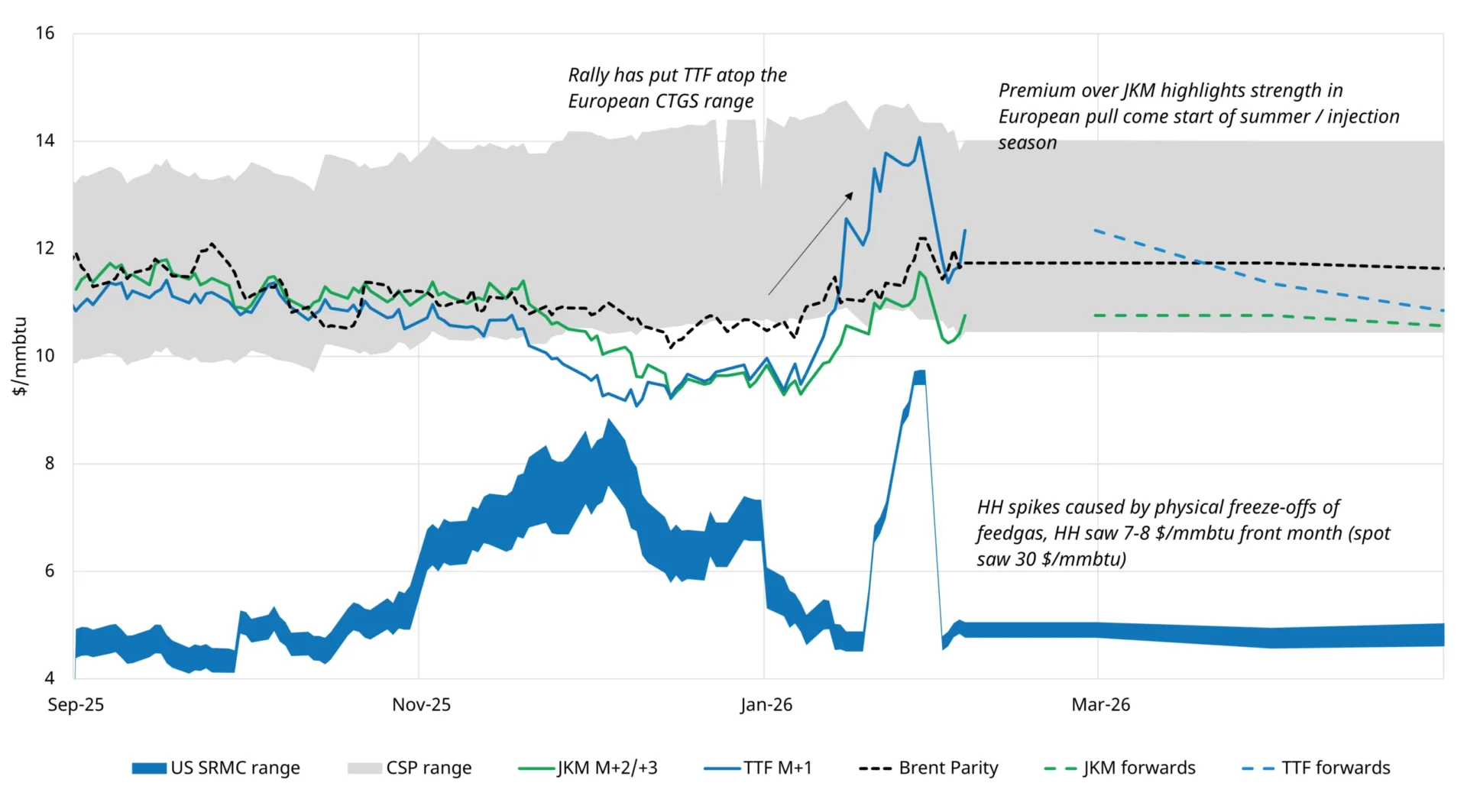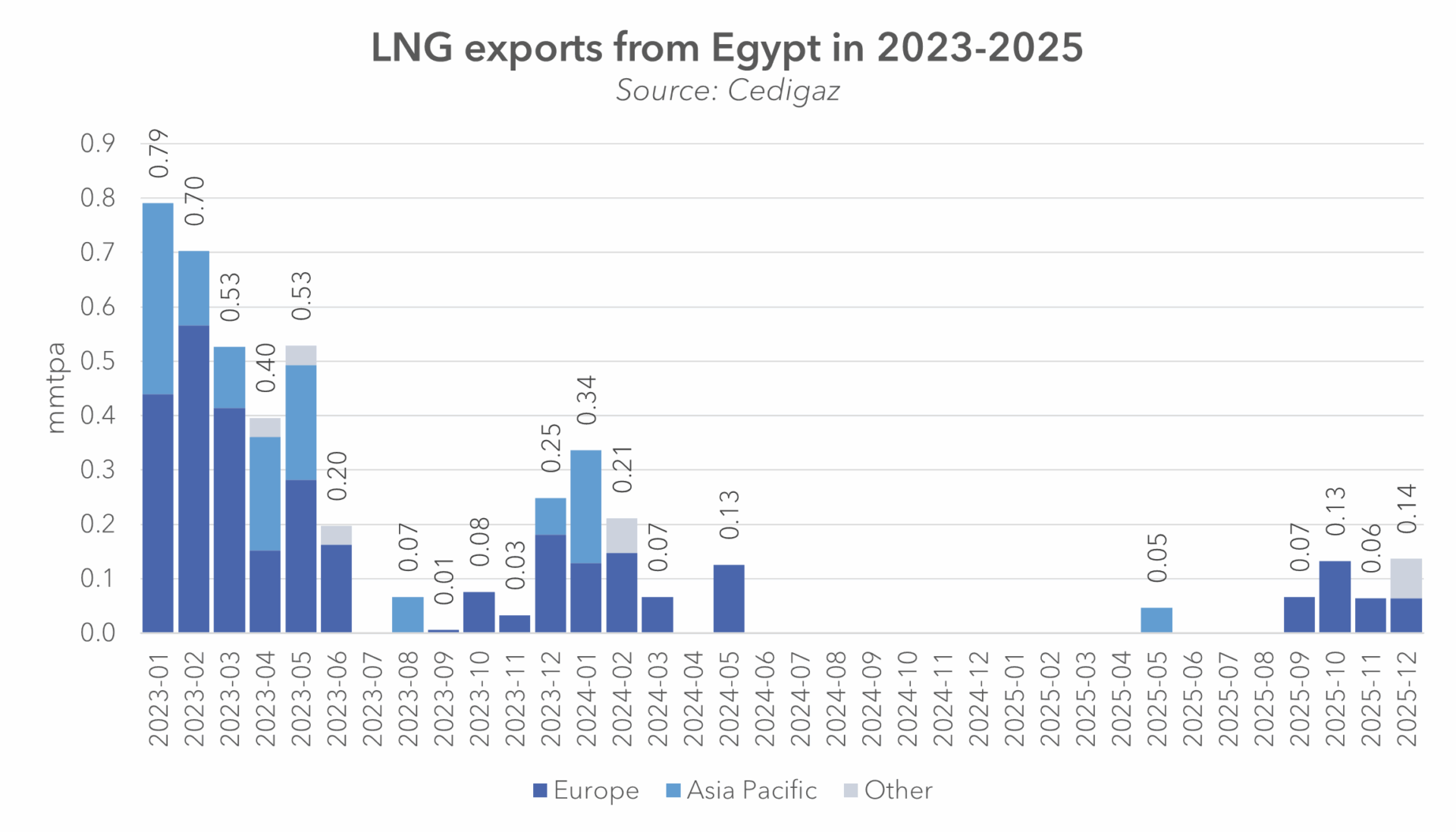

This paper presents a full life cycle assessment for greenhouse gas emissions from this exported LNG. These emissions depend on the type of tanker used to transport the LNG, with emissions far larger when LNG is transported by older tankers burning heavy fuel oil. The largest source of emissions in this case is from venting of methane lost by evaporation […]